Hydrazine Replacement
The search for more green alternatives to hydrazine has become a priority around the world in the last decade.
Due to the high quantities and concentration used for inhibiting corrosion in power generation plants and released into the environment, it does have long-term harmful effect on the environment or its biological diversity.
Feel free to check the detailed list of restrictions and regulations for hydrazine.
Hydrazine Replacement in Boiler Water Treatment
For decades, hydrazine has been used in boiler water treatment for its oxygen scavenging properties, helping reduce corrosion in feedwater and steam systems. However, due to its high toxicity, carcinogenic potential, and growing regulatory restrictions, industries worldwide are seeking safer and more sustainable alternatives.
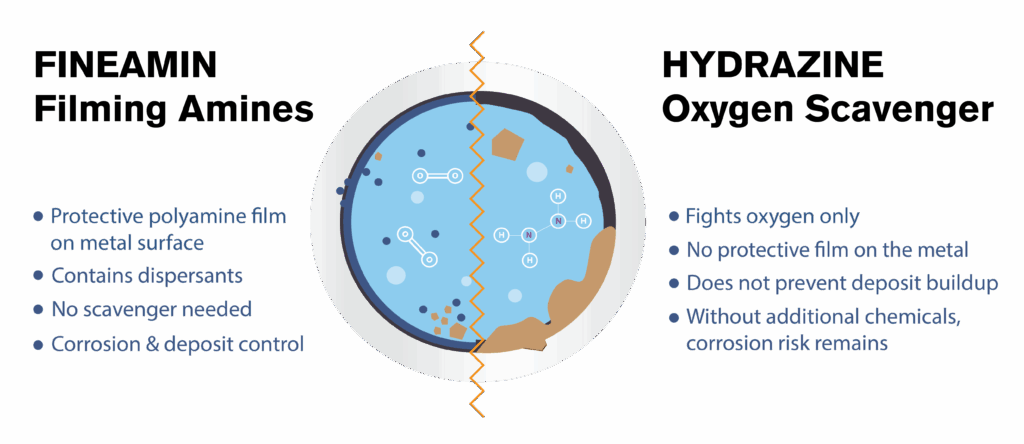
FINEAMIN offers a new generation of filming amine-based treatments that not only replace hydrazine, but also provide enhanced corrosion protection, operational efficiency, and environmental compliance.
What Is Hydrazine?
Replacing Hydrazine?
Hydrazine is a chemical compound (N₂H₄) used in boiler systems as a powerful oxygen scavenger. It helps protect metal components from oxygen-induced corrosion, especially in high-pressure steam circuits.
Common Applications:
- Power plants
- Refining and petrochemical industries
- Steam production in food and pharma
How It Works:
Hydrazine reacts with dissolved oxygen in water, converting it into nitrogen and water. This removes oxygen but does not form a protective layer on metal surfaces, leaving parts of the system vulnerable.
N₂H₄ + O₂ → N₂ + 2H₂O
Why is hydrazine being replaced? Despite its effectiveness as an oxygen scavenger, hydrazine is considered to pose serious health, safety, and environmental concerns worldwide.
Main Reasons for Replacement:
- Toxic and carcinogenic: Exposure can affect the liver, nervous system, and is classified as a Category 1B carcinogen under REACH (EU)
- Strict handling requirements: Requires controlled storage, personal protective equipment (PPE), and monitoring
- Environmental impact: Residual hydrazine or its byproducts may affect water systems and ecosystems
- Regulatory pressure: Increasingly banned or restricted across the globe
As industries aim for safer, greener, and more sustainable solutions, the search for effective alternatives has accelerated.
Fineamin - A Safe & Efficient Hydrazine Replacement
Fineamin offers a complete line of possible substitutions for hydrazine, filming amine-based chemical treatments that successfully replace hydrazine and go beyond oxygen scavenging to protect the entire water-steam cycle.
✔️ How It Works:
Fineamin’s polyamines form a microscopic protective film on metal surfaces throughout the system. This film:
- Prevents both oxidation and acid corrosion
- Reduces scaling
- Ensures smoother operation with less chemical dosage
Some formulations also include neutralizing amines and mild oxygen scavengers, ensuring full system protection without toxicity.
Benefits of Fineamin over Hydrazine
| - | Hydrazine | Fineamin |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen scavenging | ✅ | ✅ (Case by case) |
| Film-forming protection | ❌ | ✅ |
| On-line dispersing | ❌ | ✅ |
| Corrosion inhibition | Fair | Comprehensive |
| Toxicity | High | Non-toxic |
| Handling | Strict handling and storage protocols: | Easy and safe |
| Regulatory status | Restricted use | Globally accepted |
| Multi-metal protection | ❌ | ✅ |
| Effects on humans | May cause cancer. Toxic by inhalation, skin contact, and ingestion. Causes burns. Even short-term exposure may cause headaches, nausea, pulmonary edema, seizures, or coma. Acute exposure may lead to destruction of the liver, kidneys, or central nervous system. The liquid is corrosive and may cause dermatitis. Effects on the lungs, liver, spleen, and thyroid have been reported in animals exposed to hydrazine by inhalation. | Corrosive and irritating. Long-term exposure may cause burns or irritation to the respiratory system. Possible sensitization through skin contact. |
| Efects on the environment | Very toxic to aquatic organisms and may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment. | Ecological, 90% biodegradable. Water hazard class 1: low hazard. Generates no dangerous decomposition products. |
Searching for hydrazine alternatives?
Contact us for more information on how filming amines can replace hydrazine (and phosphates) in boiler water treatment.
